Miriam Duany Timosthe2
Gloria Guerra Mercado2

Translated from the original in Spanish
Original article
Educational strategy for the development of self-determination in students with intellectual disabilities
Estrategia pedagógica para el desarrollo de la autodeterminación en los educandos en situación de discapacidad intelectual
Estratégia pedagógica para o desenvolvimento da autodeterminação em alunos com deficiência intelectual
Deyanira Duverger
Calderín1![]() https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7521-1465
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7521-1465
Miriam Duany Timosthe2![]() https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6251-7019
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6251-7019
Gloria Guerra Mercado2![]() https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1729-0409
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1729-0409
1 Provincial Directorate of Education, Santiago de Cuba
![]() calderin@dpe.sc.rimed.cu
calderin@dpe.sc.rimed.cu
2 University of Oriente, Santiago de Cuba. Cuba
![]() miriamd@uo.edu.cu; gloriagm@uo.edu.cu
miriamd@uo.edu.cu; gloriagm@uo.edu.cu
| Duverger Calderín, D., Duany Timosthe, M., Guerra Mercado, G. (2024) Educational strategy for the development of self-determination in students with intellectual disabilities. Mendive. Journal of Education, 22(2), e3651. https://mendive.upr.edu.cu/index.php/MendiveUPR/article/view/3651 |
Received: October 3, 2023
Approved: April 29, 2024
ABSTRACT
The dizzying development of the scientific-technical revolution and its impact on the educational sphere require the continuous improvement of the directors of special education educational institutions, since it is their responsibility to scientifically direct the educational processes, advise teachers, families and coordinate with the socio-educational agents of the school network to achieve in students the development of practical-social skills and quality learning for life, so that they graduate fit and capable of interacting appropriately in their socio-family environment. Hence, the need to implement actions aimed at the professional improvement of the director. The article exposes a pedagogical improvement strategy to transform the modes of action of special education managers in the direction of scientific-methodological work aimed at the development of self-determination skills in students with intellectual disabilities. Theoretical and empirical methods were used to identify and solve the improvement needs of managers. The novelty of the strategy lies in the articulated conception of the different forms of improvement, established in Advanced Education, from the municipality's work system, with a systemic, planned and conscious character. With its implementation, the professional and personal performance of the managers and students was improved, who graduated with the empowerment of skills for making decisions, making choices, solving problems and establishing goals and objectives.
Keywords: Pedagogical strategy; improvement; self-determination and intellectual disability.
RESUMEN
El vertiginoso desarrollo de la revolución científico técnica y su incidencia en la esfera educacional exigen de la superación continúa de los directores de las instituciones educativas de la educación especial, pues a ellos les corresponde dirigir científicamente los procesos educativos, asesorar a docentes, familias y coordinar con los agentes socioeducativos de la red escolar para lograr en los educandos, el desarrollo de habilidades prácticas - sociales y un aprendizaje de calidad para toda la vida, de manera que egresen aptos y capaces de interactuar adecuadamente en su entorno socio familiar. De ahí, la necesidad de implementar acciones orientadas a la superación profesional del director. El artículo expone una estrategia pedagógica de superación dirigida a transformar los modos de actuación de los directivos de la educación especial para direccionar el desarrollo de habilidades de autodeterminación en los educandos en situación de discapacidad intelectual. Fueron empleados métodos del nivel teórico y empírico para la identificación y solución de las necesidades de superación de los directivos. La novedad de la estrategia radica en la concepción articulada de las diferentes formas de superación, establecidas en la Educación de Avanzada, desde el sistema de trabajo del municipio, con un carácter sistémico, planificado y consiente. Con su implementación se perfeccionó el desempeño profesional y personal de los directivos y los educandos quienes egresaron con el empoderamiento de habilidades para la toma de decisiones, la realización de elecciones, la resolución de problemas y el establecimiento de metas y objetivos.
Palabras clave: Estrategia pedagógica; superación; autodeterminación y discapacidad intelectual.
RESUMO
O vertiginoso desenvolvimento da revolução técnico-científica e o seu impacto na esfera educativa exigem o aperfeiçoamento contínuo dos dirigentes das instituições de ensino de educação especial, uma vez que lhes compete dirigir cientificamente os processos educativos, aconselhar os professores, as famílias e coordenar com o sector sócio-económico. -os agentes educativos da rede escolar conseguirem nos alunos o desenvolvimento de competências prático-sociais e uma aprendizagem de qualidade para a vida, para que se formem aptos e capazes de interagir adequadamente no seu ambiente sócio-familiar. Daí a necessidade de implementar ações que visem ao aperfeiçoamento profissional do diretor. O artigo expõe uma estratégia de aprimoramento pedagógico que visa transformar os modos de atuação dos gestores de educação especial para direcionar o desenvolvimento de competências de autodeterminação em alunos com deficiência intelectual. Métodos teóricos e empíricos foram utilizados para identificar e solucionar as necessidades de melhoria dos gestores. A novidade da estratégia reside na concepção articulada das diferentes formas de melhoria, estabelecidas na Educação Avançada, a partir do sistema de trabalho do município, com caráter sistêmico, planejado e consciente. Com a sua implementação, melhorou-se o desempenho profissional e pessoal dos gestores e alunos, que se formaram com a capacitação de competências para tomar decisões, fazer escolhas, resolver problemas e estabelecer metas e objetivos.
Palavras-chave: Estratégia pedagógica; superação; autodeterminação e deficiência intelectual.
INTRODUCTION
Currently, special education, more than a type of teaching, implies an entire educational policy, didactics for people with special educational needs in any context in which they find themselves. Special education is a way of teaching, enriched by the use of all the necessary resources, support, creativity that each case requires and enriching because it leads and transforms, develops at the peculiar pace of each student, but permanently and optimizes their odds. (Orozco, 2008, as cited in Triana Mederos & Fernández Silva, 2019, p.8)
This definition is consistent with the current Cuban social model, which assumes what is expressed in objective 4 of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, which has as its essence "guaranteeing inclusive, equitable and quality education and promoting learning opportunities throughout life." life for all." (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, 2015, p.4). In this sense, a broad vision is offered of the contexts in which educational attention to students with special educational needs operates, emphasizing the individualized and differentiating character that this education must distinguish, based on the use of resources and supports, according to each case requires it.
It is necessary to highlight that one of the challenges that inclusive education demands today is, precisely, the strengthening of the improvement of the director of the educational institution, to face the challenges of caring for students with special educational needs. In the specific case of educational institutions that serve students with intellectual disabilities, they are currently experiencing a process of change and innovation based on the implementation of a new inclusive educational model, which among its demands contains the incorporation of the concept of quality. of life as a basis to introduce the search for quality education.
Faced with this challenge, the director of this type of institution must be prepared, since it is up to him to direct this process with the use of varied procedures, the use of increasingly democratic and participatory management methods and styles, as well as the use of the necessary resources and supports for each student, according to their potential and needs.
It is also recognized that this process of change is coherent with the demands of the Third Improvement of the Cuban Educational System, which has generated in special schools, transformations in the organizational structure, the curriculum and the content, based on experimentation, implementation and then systematization of new forms in the scientific methodological work system as a way of preparing and improving teachers and managers; in working with the institutional curriculum; in the dynamics with the socio-educational network; in working with families and in the progress of an educational process with a developmental nature; Therefore, the institutional educational project requires the participation and decision of all educational agents and agencies that influence the comprehensive development of students with intellectual disabilities; in addition to taking into account the means, resources and support for access to the curriculum, the accessibility of physical spaces and the availability of individualized attention areas to increasingly guarantee the quality of life of students based on their social inclusion. .
This process of change presupposes a radical transformation in the thinking and actions of special education managers, which makes evident the need to raise new and more complex demands on their professionalism, which can be achieved with the improvement of actions. aimed at their improvement.
Schools where educational attention is provided to students with intellectual disabilities assume the end of special education, going beyond the traditionalist conception, generated by the current economic, historical, political and social circumstances. Its purpose is to achieve the maximum possible comprehensive development of people with special educational needs associated or not with a disability, in any context, which allows them to face their social inclusion with various levels of independence, in accordance with the purpose and objectives. of each educational level.
In this sense, Triana Mederos & Fernández Silva (2019) highlight that "one of the objectives assumed by special education is to manifest the maximum possible development in correspondence with their individual characteristics that makes it easier to solve the problems of daily life." (p. 14)
Intellectual disability has been assimilated to replace that of mental retardation, accompanied by its definition, understood as:
A relatively stable condition of development that is characterized by significant limitations and of different degrees in intellectual activity, in general, and in the acquisition of conceptual, practical and social learning revealed in the modes of social action, in particular; who require support of varying intensity throughout life. It is characterized by variability and differences in expression in functioning. It arises before the age of 18. Its degree of depth is related to the intensity of the support that a person needs throughout their life. (Leyva, 2018, p. 10)
Indeed, the definition emphasizes the use of resources and supports, throughout life, necessary for the acquisition of conceptual, social and practical learning that is associated with life skills, revealed in the modes of action. social, which, according to Leyva (2018), are defined as:
The way of applying conceptual, social or practical learning in social activity; that determine the way in which a person behaves and is more or less capable of facing life situations independently, in accordance with social norms for a uniform environment and group, which allows him or her to participate in activities with the fewest limitations and restriction on social participation (p. 10)
One of the life skills that requires being oriented and trained in the direction of the teaching-educational process is self-determination, which refers to the set of activities and skills that the person needs to act autonomously and be the protagonist of events. relevant aspects of their life, without unnecessary external influences ( Wehmeyer, 2009, p. 53).
The development of this skill becomes more relevant, as long as different educational strategies and forms of organization are implemented that offer students opportunities to develop a greater sense of responsibility for making correct decisions in the face of problems and conflicts, making choices, managing stressful life situations, be autonomous, independent, know themselves and establish appropriate interpersonal relationships.
The fulfillment of the purpose and objective set out above demonstrates the need for continuous and permanent improvement of the director, so that they acquire a solid scientific methodological and methodological teaching preparation that allows them to influence the professional development of subordinate structures, as well as scientifically direct the instructional-educational processes, advise families and coordinate with the socio-educational agents of the school network to achieve in students with intellectual disabilities the development of practical-social skills and quality learning for life, so that They graduate fit and capable of interacting appropriately in their social and family environment.
With respect to professional improvement, López (2019), states in his studies that the improvement of directors, who are also teachers, "has as its purpose the development of the subject for his professional and human improvement and its objectives are aimed at expanding, perfect, update, complement knowledge, skills and abilities, consolidate values, promote development and professional modes of action " (p.2.)
Valiente (2003) specifies that "professional improvement is a continuous, prolonged, permanent process that occurs during the performance of teaching or managerial functions, unlike training, which constitutes an initial stage of preparation in the development of the teacher." or director who may precede at the time of assuming them". (p. 54)
For Añorga (2014), professional development is "the set of teaching-learning processes that enables university graduates to acquire and continuously improve the knowledge and skills required for better performance in their work functions, as well as for their development." general culture." (p.2)
For their part, Cruz et al. (2018), states that "professional improvement can be conceived as an educational process, contextualized, intended to improve professional performance (...), to respond to the social task that today demands a quality service in Cuba and the world, in the fulfillment of their healthcare, teaching, research and managerial functions (...)" (p. 4)
In this regard, the authors assume the definition given by Cruz et al. (2018) when proposing that professional suppuration constitutes an educational process of transformation of the director and the school context in which he acts, aimed at improving his professional performance, so that he is put in better conditions to direct the objectives and guidelines with quality. that today the educational system and society demand from the schools where students with intellectual disabilities are served.
Taking the previous definitions as references and in the particular case of the technical and management staff of special schools, the process of professional development is considered one of the most important activities to plan and develop within each level and educational institution. considering as essential elements, the updating of knowledge and professional skills, which are necessary for the performance of the director's responsibilities and job functions. Its content is determined based on the personalized needs of the manager and the demands that special education demands for the care of students with intellectual disabilities.
The importance that the concept of continuous improvement of managers and teachers in the educational system acquires in recent times is a topic that has been addressed by researchers from different latitudes of the world, such as: Valiente (2003), Añorga (2014), Bernaza (2020), Maiga (2021), Lozada, Huepp and Fumero (2022), Rivero (2024), among others.
Their contributions consist of offering the theoretical foundations that support the process of professional improvement of Higher Education teachers; pedagogical and theoretical methodological models to raise the professional improvement of teachers and directors, pedagogical strategies for the improvement of speech therapists who serve students with hearing disabilities, alternative psych pedagogical advice aimed at preparing the teacher for the educational inclusion of students with autism spectrum disorder; for the design of curricular adjustments; for the improvement of pedagogical communication with a personological approach as well as for the strengthening of professional guidance and vocational training.
However, the documentary review reveals a small number of investigations that allow defining the establishment of improvement proposals for the director of the special school that facilitates him guiding, from his management functions, the development of skills for self-determination in the students. in a situation of intellectual disability, from the implementation of learning and educational strategies and the appropriate methodologies to achieve it.
When carrying out an analysis of the improvement system designed for directors who work in special schools, it was found that:
An aspect that supports the previous reality is reflected when the student graduates from the educational institution, showing little participation in everyday life situations that involve choices according to their interests, tastes and desires, restricted environments in which these people can apply the acquired knowledge. to new everyday situations and insufficient options to acquire a broader repertoire of alternatives for the solution of a conflict.
Every year, several students with intellectual disabilities graduate from special schools who do not achieve quality incorporation into an ordinary job, among other reasons, because they have not developed the social skills and work habits required by job positions. that are offered in employment offices, in addition to there being a percentage of graduates who present job instability. The study programs of the different subjects and other complementary activities are fundamentally focused on the development of work and academic skills, not the development of socio-affective skills such as self-determination.
Taking into consideration the aforementioned, the insufficiencies in the improvement process of the director of special education that limits his preparation for the development of self-determination skills in students with intellectual disabilities are determined as a scientific problem.
Therefore, the objective of this work is revealed to be the presentation of a pedagogical improvement strategy for the director of special education, which prepares him to direct the development of self-determination skills in students with intellectual disabilities.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
For the development of the proposal, a population of 36 directors of special schools where educational attention is provided to students with intellectual disabilities in the province of Santiago de Cuba, 12 municipal methodologists of special education in the territory, was selected as a unit of analysis. and 1 advisor from the Municipal Directorate of Santiago de Cuba which attends to the improvement activity. The sample was made up of 19 directors, 5 methodologists from the main municipality, Santiago de Cuba, and 1 municipal advisor, responsible for the improvement activity.
The research was mixed. Its logic is based on the Materialist Dialectical approach that enabled the most effective use of methods and techniques to delve deeper into the object of study from a scientific position, in addition to facilitating the determination of causal and functional relationships in the dynamics of the process. of professional improvement of the directors of special schools, as well as the establishment of the essential and contradictory relationships that occur in this.
To fulfill the tasks, different research methods and techniques at the theoretical, empirical and statistical level were used, which favored the processing of information. These are detailed below:
Theoretical methods: Analysis-synthesis, historical-logical, inductive-deductive, dialectical materialist and systemic structural functional. These made it possible to establish the methodological theoretical references that characterize the process of professional improvement of directors, as well as to determine and prioritize the stages and the system of actions that structure the pedagogical strategy.
The analysis - synthesis was used with the purpose of substantiating the methodological theoretical references that characterize the improvement process of the directors and identifying the regularities of the initial and final diagnosis of the scientific problem in terms of needs and potentialities.
The logical history was used with the objective of studying the historical background of the directors' improvement process in the specific socio-historical conditions through which it has gone.
The inductive deductive encouraged the study of the particular and singular phenomena that characterize the scientific problem, in order to infer or confirm theoretical formulations to reach logical conclusions.
The dialectical-materialist method was used in the development of the entire investigation, to determine its dynamic elements and significant relationships, in addition to being an expression of the logic followed in the construction of the scientific knowledge achieved.
The functional systemic-structural method was used to structure, in a coherent manner, the proposed improvement strategy based on the results of the diagnosis of the state of the directors' improvement and the interrelation between its components, with a system character, dependency, hierarchy. and structuring, as well as the relationships and interdependence between the contents.
The empirical methods allowed diagnosing and evaluating the initial and final state of the preparation of managers to direct the development of self-determination skills in students with intellectual disabilities.
To collect the information, documentary review, observation of improvement activities, a survey of directors and group and individual interviews with directors, municipal methodologists of special education and the improvement advisor of the Santiago de Cuba municipality were used.
We worked on the analysis of the current state of the research problem with the use of the aforementioned instruments, which favored the collection of data and evidence. They were previously designed; Then the information was processed and the results were evaluated and interpreted, all of which led to the determination of an inventory of problems in the improvement process of the directors of the special schools.
With the objective of guiding the diagnosis, the indicators to be measured were determined, in correspondence with the assumed scientific problem and its close relationship with the defined object and field; which were taken into account in the instruments developed and applied.
Below, we refer to the indicators that were taken into account:
1. Planning, organization and control of improvement.
2. Knowledge and use of ways to improve.
3. Contents taught in the improvement.
4. Mastery and treatment of self-determination skills during the improvement process.
5. Diagnosis and characterization of the directors of special schools.
6. Correspondence between the needs, the directors' individual improvement plan and the improvement offers.
7. The role of the municipal structure in the improvement of directors.
8. Level of satisfaction with the improvement that is carried out.
9. Level of effectiveness in improvement based on the successful achievement of the special school for students with intellectual disabilities.
The documentary review was used with the objective of analyzing and verifying the organization, content and monitoring of the improvement designed for directors based on what is established in the ministerial resolutions of the Ministry of Education (MINED) and the Ministry of Higher Education (MES). In addition to the regulatory documents, the reports of the methodological assistance visits (VAM) by the municipal department of special education during the school years (2018-2019 and 2021-2022) were reviewed; the improvement strategies designed for the directors of special schools conceived by municipal and provincial bodies; the minutes of the Technical and Management Bodies of educational institutions; the class systems and curricular activities conceived by the teachers and the individual improvement plans of the 15 directors of the Santiago de Cuba municipality, intentionally chosen from the selected sample, which represents 78.9% of it.
9 improvement activities designed for the directors of special education were observed, distributed in: 3 observations on the development of improvement courses, 4 observations on the development of methodological meetings, all carried out by the Municipal Special Education Department and 2 observations on the development of the methodological help visits carried out in educational institutions with the objective of verifying how it manifests itself in practice and the causes that originate the problem under investigation. Participant observation was applied in the development of the VAM to verify the transformations that are occurring in the directors' modes of action, as a result of the implementation of the different forms of improvement proposed in the pedagogical strategy.
The objective of the survey was to obtain information about the improvement activities carried out with directors, as well as the treatment offered to the development of self-determination skills in the different improvement activities carried out. It was applied to the 19 directors who are part of the selected sample, which represents 52.7% of the total directors who work in this type of specialty.
The purpose of the group and individual interview was to obtain information about how and what elements are taken into account in planning the improvement of directors, their effectiveness, as well as to determine the improvement needs that they have. Five municipal methodologists from the special education department in Santiago de Cuba were interviewed in groups, as well as the municipal advisor who oversees the improvement activity of the municipality itself. The individual interview was applied to 15 special education directors, chosen at random.
As a mathematical method, percentage analysis was applied with the objective of carrying out all the processing and interpretation of the data obtained in the diagnosis to access a qualitative assessment of them.
RESULTS
The results obtained, from the application of the methods, techniques and instruments used to verify the problem, facilitated the subsequent methodological triangulation of the information. The following results were found:
To evaluate the improvement variable, some indicators were defined and the scale was taken into account: Very Adequate (MA); Fairly Adequate (BA); Adequate (A); Poorly Suitable (PA); Inadequate (I).
Table 1- Observation of the development of improvement activities.
No. |
Indicators |
M.A. |
B.A. |
TO |
P.A. |
Yo |
1 |
If the results of the diagnosis and the characterization of the directors are taken into account for their differentiated attention. |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
7 |
2 |
If the objectives and contents that are developed respond to the needs of the directors. |
- |
- |
1 |
6 |
2 |
3 |
Treatment provided to self-determination skills (control and evaluation) |
- |
- |
7 |
2 |
|
4 |
If it offers the director the theoretical and methodological tools and instruments to direct the development of self-determination skills. |
- |
- |
5 |
4 |
|
5 |
Forms of organization, control and evaluation that are used. |
- |
1 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
6 |
Correlation between the different forms of improvement. |
- |
- |
5 |
4 |
|
7 |
self-preparation tasks in the improvement actions developed. |
- |
- |
1 |
6 |
2 |
The results of the diagnostic study made it possible to identify the scientific problem, hence the need to overcome the directors through a pedagogical improvement strategy that prepares them to direct the development of self-determination skills in students with intellectual disabilities.
The proposed pedagogical improvement strategy is structured taking as a reference the conception assumed by De Armas and Valle (2011), stating that:
The strategies are designed to solve practical problems and overcome difficulties with optimization of time and resources, they allow projecting a qualitative change in the system, by eliminating contradictions between the current state and the desired one, they imply a planning process in which the establishment of sequences of actions oriented towards the goal to be achieved occurs ... (p. 34)
In this regard, the authors of this work define the pedagogical improvement strategy as: the system of closely related actions that will satisfy the improvement needs of the directors of special schools in order to transform their modes of action in the direction of the development process. teaching-learning and educational for the development of self-determination skills in students with intellectual disabilities. Its design is based on the diagnosis of needs and the preparation of directors, a general objective is required, the deadlines for its execution, those responsible and the actions that comprise it will be systematically controlled and evaluated to transform the existing reality from a current state to a desired one.
For the structuring of the pedagogical strategy for improvement and the elaboration of its theoretical foundations, the philosophical, sociological, psychological and pedagogical sciences were taken as a basis, which allowed from a theoretical point of view to provide coherence, scientificity and organization in the planning of the actions that make it up. The criterion of personality was taken into account as a social product in which subject-object, subject-subject interact dialectically, under the influence of different educational agents and takes as a premise that this is formed in and by activity, where the cognitive and the affective form a unit, proposes the personological approach that implies not only the recognition of the profession, its meaning in the social context, the importance of its existence in life, but also its regulatory function in the subject's activity.
As Valiente (2003) states, "the pedagogical strategy for improving special education directors takes into account the comprehensive and systematic approach to the components of the pedagogical process" (p.52). For this it is assumed:
On the other hand, the authors assume what was expressed by López et al. (2023), stating that:
The pedagogical strategy is a consistent way of articulating psychopedagogical intervention processes, which result in the establishment of a helping relationship, either individually or in groups to achieve higher levels of human development and personal growth. (p. 3).
From this perspective, the proposed pedagogical strategy takes into account the role of educational practice and its link with theory and the necessary interaction of instruction, education and development to achieve the preparation of directors based on the development of self-determination skills in students with intellectual disabilities.
Great importance was given to social factors, the interrelation between the affective and the cognitive, the role of experience, communication and activity in the development of personality. In this sense, the principles of pedagogy as a science, proposed by Addine (2021), were considered. It should be noted that these principles are general (feasible to apply at any level of teaching, grade and subject) and essential (considers the non-personal components of the educational process); Furthermore, they have system character. These principles are:
1. The unity of the scientific and ideological character of the pedagogical process.
2. The connection of education with life, the social environment and work in the process of personality education.
3. The unity of the instructive, the educational and the developmental in the process of personality education.
4. The unity of the affective and the cognitive in the process of personality education.
5. The collective and individual nature of education and respect for the personality of the student.
6. The unity between activity, communication and personality (p. 83).
The strategy was implemented in the work system of the Municipal Directorate of Education of Santiago de Cuba and was executed by teachers from the special education department of the Faculty of Early Childhood Education of the University of Oriente, advisors from the Diagnosis and Guidance Center, provincial educational methodologists, in two school years. It contains a system of actions, structured in four stages, which, in response to the diagnosed improvement needs, linked the different forms of professional improvement where various educational strategies aimed at the development of self-determination skills were modeled, designed and socialized through workshops. in students with intellectual disabilities, based on what is stated in the graduate profile. Its evaluation was carried out through the workshops themselves and in the performance of the directors' functions.
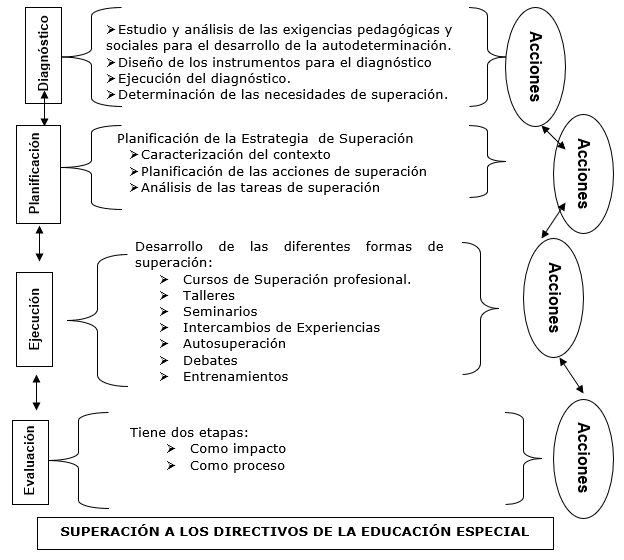
Fig.1 - Dynamics of the pedagogical strategy for the improvement of special education directors
In the diagnosis stage, the instruments were developed, applied, and the needs and potentials in the level of preparation of the directors were determined based on the study and analysis of the pedagogical and social demands for the development of self-determination skills in the students. in a situation of intellectual disability. In the same way, the documents and strategies that regulate the design and execution of the improvement of managers were studied.
Subsequently, we proceeded to the planning stage where individual improvement plans were designed in accordance with the individual results of the diagnosis. To the same extent, the actions of the strategy were projected, considering as a central axis in its content, the theoretical methodological foundations and the management tools and practices that allow the director to guide the development of self-determination skills, from the management functions. . The objectives, responsible persons, contents, organizational and evaluation forms were defined. The planning of the improvement activities was conceived, based on the conception and articulation of the different forms of improvement that appear reflected in Advanced Education, written by Julia Añorga and later taken up by other researchers such as Cardoso, Valdés and Panesso (2022), among which are workshops, seminars, courses, self-improvement, debates and exchange of experience. They were grouped into three levels: theoretical, practical and systematization. 6 workshops, 3 seminars, 1 course were planned, the latter was implemented in the directors' school, with the use of participatory techniques, debates, exchanges. Self-improvement was directed from the topics worked on in the different forms of improvement. In the design of the methodological help visits, the topics developed in the directors' school, in the workshops and seminars were taken into account, giving the improvement process a system character.
In the execution stage, the improvement actions designed in the previous stage were implemented. They were linked to each other, for example, in the development of the workshops, debate was applied and individual activities were guided for the development of self-improvement, in addition, the four moments mentioned Vega et al. (2018), they are: individual reflection, collective reflection, work in small groups and the plenary session. (p.13). The exchange of experience as an action for improvement was carried out in the scientific events and seminars held, where the directors presented their pedagogical experiences related to the development of self-determination skills.
In carrying out the improvement activities and as a form of evaluation, scientific production was intended for the directors, based on the preparation of scientific articles, complementary programs, consultation materials for teachers and families, exercise systems and others; all aimed at developing self-determination skills in students with intellectual disabilities.
The fourth stage: called Evaluation, aimed to evaluate the knowledge and skills achieved by the directors, based on the application of improvement actions to effectively develop self-determination skills in the students. Evaluation was considered as a process and as a result, the latter valued based on its impact on the professional performance of managers.
DISCUSSION
In the Regulations of Postgraduate Education of the Republic of Cuba (2019), the Ministry of Higher Education reaffirms that "professional improvement aims at the permanent training and systematic updating of university graduates, the improvement of the performance of their professional and academic activities, as well as the enrichment of its cultural heritage" (p. 4)
Therefore, the professional development of special education directors constitutes a priority that ensures the acquisition, expansion, updating and continuous improvement of the professional knowledge and skills required to carry out the professional work they perform. All actions developed in favor of the preparation of managers must be put in better conditions to enhance the development of subordinate structures and teachers so that in this way they can guide, lead, promote and accelerate development. of their students and guidance to families based on the formation and development of habits, skills, values and standards of behavior.
One of the findings of the study carried out is that, in Cuba, to date, the development of self-determination skills in students with intellectual disabilities is a topic that has been very rarely addressed from the conception of study plans and programs for work. in this specialty. The pedagogical proposals for their theoretical-methodological treatment are also insufficient, given the lack of intentionality from the direction of professional improvement towards the directors and teachers who work in schools that provide educational care to students with intellectual disabilities, for example. which is evident the need to overcome them in this sense, so that they can teach and guide theory and practice on the particularities that characterize the development of self-determination skills and, in the exercise of their profession, apply didactic, educational, the methods, procedures, teaching aids and various organizational forms in order to achieve the development of these skills in students and create the bases to ensure quality in school graduation.
There have been many researchers who have ventured into the topic related to the professional development of managers. In the case of (Valiente, 2003), he provides a systemic conception of the improvement of Basic Secondary School principals. The continuous training of decent people for quality education has been studied by (Urday-Cáceres and Tenorio-Guevara, 2022); The professional development of the speech therapist to care for students with hearing disabilities has been investigated by (Lozada et al., 2022). Obviously, these contributions offer the tools and methodological procedures for deepening, updating and perfecting the professionalism of the director of the educational institution.
When comparing the results of the aforementioned studies with the pedagogical improvement strategy proposed by the authors of this research, we consider that there are coincidental aspects, related to the theoretical, methodological and didactic foundations that support the process of professional improvement of managers, as well as as, of the need to permanently overcome them; However, in the consultations carried out on these and other investigative works, in general, the number of works referring to the preparation, in scientific management, of the directors of special schools, related to the development of self-determination skills in students, is very small. learners with intellectual disabilities.
By way of conclusion, the pedagogical strategy socialized in this article aimed to prepare directors to transform their modes of action in the direction of scientific-methodological work aimed at the development of self-determination skills in students with intellectual disabilities. The diagnosis carried out reflects insufficiencies in the design and content of the organizational forms of improvement, which do not satisfy their needs based on the development of self-determination skills in students with intellectual disabilities. The organizational forms of improvement implemented, as part of the pedagogical strategy, provided the directors with the necessary tools, in terms of management, to lead the development of the aforementioned skills. The feasibility and relevance of the pedagogical strategy were verified in educational practice. The evaluation of its impact allowed us to define the results obtained in the professional performance of the managers, based on the development of self-determination skills in the students, obtaining the following effects: effective correspondence between the graduate's model and the design of the scientific work. methodological; efficient organization and better results in the teaching-educational process and in the job preparation system; quality in the egress and transit process; improvements in the orientation process for families and other community agents and positive transformation in the modes of action of the directors in general, and of the students in particular, who graduated with the empowerment of skills for decision-making, resolution of problems, to establish and achieve their objectives, as well as to make their choices based on their tastes and preferences.
REFERENCES
Añorga-Morales, J. A. (2014). La Educación Avanzada y el mejoramiento profesional y humano. Varona, 58, 19-31. http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=360634165003
Bernaza, G.J., Aparicio, J.L., De la Paz, E., Torres, A.M. y Alfonso, J.E. (2020). La Educación de Posgrado ante el nuevo escenario generado por la COVID-19. Educación Médica Superior, 34(4), 18. http://www.ems.sld.cu/index.php/ems/article/view/2718
Cardoso Camejo, L., Valdés Naranjo, M. & Panesso Patiño. V. (2022). La teoría de la Educación Avanzada: epistemología de una teoría educativa cubana. Varona,15(49),39-52. http://revistas.ucpejv.edu.cu/index.php/rVar/article/view/1549
Fernández, F. A. (2021). La didáctica general y su enseñanza en la educación superior pedagógica. Aportes e impacto. Editorial Pueblo y Educación.
Cruz, L.C., Ramos, M., Nardiz, O. y Rivero, D. (2018). Fundamentos teóricos que sustentan el proceso de superación profesional de los tecnólogos en Podología. 22(6),1140-1148. http://revcmpinar.sld.cu/index.php/publicaciones/article/view/3468
De Armas Ramírez, N. & Valle Lima, A. (2011). Resultados científicos en la investigación educativa. Editorial Pueblo y Educación.
Leyva Fuentes, M. (2018). Manual de psicopedagogía. Material teórico instructivo para especialistas de los centros de diagnóstico y orientación. CDO. 21(4), 10. https://hdl.handle.net/123456789/2104
López Collazo, Z. S. (2019). Enfoques teóricos acerca de la superación profesional, una mirada en las áreas técnicas. Varona. Revista Científico Metodológica, 68 (1). e04. http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1992-82382019000100004&lng=es&tlng=es
López Llerena, L. L., Rodríguez Torres, E., & Herrera Arencibia, L. (2023). Estrategia pedagógica para la preparación del profesor de Educación Física como mediador de conflictos. Podium. Revista de Ciencia y Tecnología en la Cultura Física, 18(3), e1474. https://podium.upr.edu.cu/index.php/podium/article/view/1474
Lozada Ortiz, A., Huepp Ramos, F. L., & Fumero Pérez, A. (2022). Apuntes históricos sobre la superación profesional del maestro logopeda en Santiago de Cuba. EduSol, 22(81), 20-35. http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1729-80912022000400020&lng=en&tlng=es
Maiga, A. (2021). La Educación Especial en la república de Mali: antecedentes, desafíos y perspectivas. Recherches Africaines, (28 Juin), 60-67. https://www.google.es/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://revues.ml/index.php/recherches/article/view/2329/1588&ved=2ahUKEwiFgcXUkJiFAxUsg4QIHQ0FAwcQFnoECBAQAQ&usg=AOvVaw2uHjXZy96L6bPZTDLBux_7
Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Educación, la Ciencia y la Cultura. (2015). Transformar nuestro mundo: la Agenda 2030 para el Desarrollo Sostenible. http://www.unfpa.org/es/resources/transformar-nuestro-mundo-la-agenda-2030-para-el-desarrollo-sostenible-0
Resolución 140 de 2019. Ministerio de Educación Superior, Reglamento de Educación de Posgrado. Disponible en: http://www.gacetaoficial.goc.cu
Rivero, L. R. (2024). Alternativa de asesoría psicopedagógica para el trabajo con los docentes desde la inclusión educativa de adolescentes con Trastorno Espectro Autista. Joven Educador, 42(septiembre - diciembre), 1-11. http://revistas.ucpejv.edu.cu/index.php/rJEdu/article/view/1979
Triana Mederos, M. & Fernández Silva, I. (2019). La Educación Especial en Cuba: Concepción actual y perspectivas. Editorial Pueblo y Educación.
Urday-Cáceres, J. R. y Tenorio-Guevaras, T. (2022). Formación continua del docente universitario: reto y oportunidad para una enseñanza de calidad. Maestro y Sociedad, 19(3), pp. 1100-1129. http://maestroysociedad.uo.edu.cu
Valiente Sandó, P. (2003). Un modelo teórico-metodológico para la dirección de la superación postgraduada de docentes y directivos educacionales. La Habana: Editorial Pueblo y Educación.
Vega-Suárez, D., Jañez-Reyes, I., Rodríguez-Martínez, N. (2018). Sistema de acciones para la superación de los profesionales del CITMA en Guantánamo. Edusol, 18(1), 100-111. https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=6843361
Wehmeyer, M. L. (2009). Autodeterminación y la Tercera Generación de prácticas de Inclusión. Revista de Educación, (349), 45-67 http://hdl.handle.net/11162/74528
Conflicts of interest
The authors report that there are no conflicts of interest in relation to the research presented.
Authors' contribution
MsC . Deyanira Duvergel Calderín participates in the methodological and conceptual design of the work, as well as in the development, application and interpretation of the instruments for diagnosis and in the conception of the Strategy.
Dr.C Miriam Duany Timosthe contributed to deepening the foundations of the research and developing the strategy.
DrC . Gloria Guerra Mercado, contributed to the application of the instruments and development of the strategy.
![]()
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial 4.0
International License