
Mendive. Revista de Educación, octuber-december 2020; 18(4):729-745
Translated from the original in Spanish
Working for the Students discipline. Experiences in Pinar del Rio
Trabajando por la disciplina estudiantil: experiencias en Pinar del Río
Trabalhar para a disciplina estudantil: experiências em Pinar del Río
Marisol Bravo Salvador
Universidad de Pinar del Río "Hermanos Saíz Monte de Oca". Cuba. ORCID: http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0062-5057, Correo electrónico: mbravosalvador2019@gmail.com
Received: December 2th, 2019
Approved: September 7th, 2020
ABSTRACT
The educational system in our country, in response to the legal provisions of the Cuban State for the administration of justice to minors, serves as a substantive process of preventive and community work, an essential process for the comprehensive formation of current and new generations. The present article aims to socialize a strategy to prevent the aggravation of indiscipline in students from the province of Pinar del Río. Methods such as document analysis, systemic approach, interview, observation, case study, and analysis-synthesis and induction-deduction procedures were used to find out about preventive work, identify and characterize students who do not comply homework as well as its evolution after applying the strategy. In conclusion, the proposed strategy to prevent the aggravation of indiscipline in students, with an interactive and multifactorial nuance, based from a developing perspective, on the Cuban experience on preventive work makes it viable for the fulfillment of the stated objective and feasible from its insertion in the Work System of the Provincial Directorate of Education in Pinar del Río.
Key words: indiscipline; school duties; conduct disorders; administration of juvenile justice; prevention; School Council; Preventive work group.
RESUMEN
El sistema educacional en nuestro país en respuesta a las disposiciones legales del Estado Cubano para la administración de justicia a menores, atiende como proceso sustantivo el trabajo preventivo y comunitario, proceso esencial para la formación integral de las actuales y nuevas generaciones. El artículo que se presenta tiene como objetivo socializar una estrategia para prevenir el agravamiento de las indisciplinas en estudiantes de la provincia de Pinar del Río. Métodos como el análisis de documentos, el enfoque sistémico, la entrevista, la observación, el estudio de casos y los procedimientos análisis-síntesis e inducción-deducción, fueron utilizados para conocer referentes acerca del trabajo preventivo, identificar y caracterizar a los estudiantes que incumplen deberes escolares, así como su evolución después de aplicada la estrategia. En conclusión, la estrategia propuesta para prevenir el agravamiento de las indisciplinas en estudiantes, con un matiz interactivo y multifactorial, fundamentada desde una perspectiva desarrolladora, en la experiencia cubana sobre el trabajo preventivo la hace viable para el cumplimiento del objetivo planteado y factible desde su inserción en el Sistema de Trabajo de la Dirección Provincial de Educación en Pinar del Río.
Palabras clave: indisciplinas; deberes escolares; trastornos de conducta; administración de justicia a menores; prevención; Consejo de Escuela; Grupo de trabajo preventivo.
RESUMO
O sistema educativo no nosso país, em resposta às disposições legais do Estado cubano para a administração da justiça a menores, trata do trabalho preventivo e comunitário como um processo substantivo, um processo essencial para a formação integral das gerações atuais e novas. O objectivo do artigo apresentado é socializar uma estratégia para evitar o agravamento da indisciplina nos estudantes da província de Pinar del Río. Métodos tais como análise documental, abordagem sistémica, entrevista, observação, estudo de casos e análise-síntese e procedimentos de indução-dedução foram utilizados para conhecer referências sobre o trabalho preventivo, identificar e caracterizar os alunos que não cumprem as obrigações escolares, bem como a sua evolução após a aplicação da estratégia. Em conclusão, a estratégia proposta para evitar o agravamento das indisciplinas nos estudantes, com uma nuance interativa e multifatorial, baseada numa perspectiva de desenvolvimento, na experiência cubana sobre trabalho preventivo torna-a viável para o cumprimento do objectivo proposto e viável desde a sua inserção no Sistema de Trabalho da Direcção Provincial de Educação em Pinar del Río.
Palavras-chave: indisciplinas; deveres escolares; perturbações de conduta; administração da justiça a menores; prevenção; Conselho Escolar; grupo de trabalho preventivo.
INTRODUCTION
Today Cuba is experiencing a transcendental historical moment of updating its Economic and Social Model of Socialist Development, characterized in its essence by the socio-productive , labor, political, legal, social, ideological and cultural rearrangement, guided by the Guidelines of the Economic Policy and Social agreed by the VI and VII Congress of the Communist Party of Cuba (PCC), based on the thought of Martí, the teaching of Fidel and Raúl and on the experiences accumulated during more than 60 years of the Revolution, as stated in the material Documents 7th Party Congress approved by the III Plenum of the PCC Central Committee on May 18, 2017 and endorsed by the National Assembly of People's Power on June 1, 2017. Compendium (PCC, 2017).
Changes framed a complex context, in which highlights the effects of the economic, commercial and financial blockade that for more than sixty years has been imposed by the Yankee imperialism; the destroyed consequences of natural phenomena; the internal economic situation; our own mistakes and negative trends that have emerged, that warn us about manifestations of social indiscipline that put in a danger growing one of the most important achievements most important reached by our people: The education.
That situation has propitiated that the Cuban Educational system, taking into account the complexity of changing conditions, stands in transverse axis prevention work and for its implementation it inserted into work system, where they come to play a major role organs functional as the groups of preventive work at different levels and School Council, where he conceived the preparation of principals, teachers, students, family and community to ensure the success of this substantive process.
They were the works of Vigotsky (1989); Castillo del Risco et al. (2013); García & Tamayo (2018); Ferrer, Martín, & Suz (2019) and the analysis of research results by Valle, Aguilartes & Rodríguez (2016); Romo, Ramos & Velázquez (2017); Almaguer & Almaguer (2017); Peña, Garcés & López (2017), which provided theoretical and practical results that support the need to seek new ways to prevent the aggravation of indiscipline in students from the province of Pinar del Río , with an interactive and multifactorial nature.
With a view from the Historic Cultural approach, the prevention is defined as: The adoption of measures to prevent their occurrence in children / girls, adolescents, youth and adults negative manifestations in behavior, development or learning from the early identification of risk factors and preventing these manifestations, when they have occurred, from having negative psychological and social consequences that compromise their comprehensive training (Castillo del Risco et al, 2013) . Four levels of prevention are declared:
First Level (Primary Prevention): measures taken when negative manifestations have not yet occurred. It is carried out in a supposedly healthy framework, but on individuals incorporated into risk groups, considering as risk an important and identifiable minimum of casual factors, of a biological, psychosocial, economic and environmental order, which associated can produce a certain alteration, compromising the normal development for children, adolescents and adults.
Second Level (Secondary Prevention): it is carried out before the appearance of alterations, to avoid that, as a consequence, a more serious manifestation appears.
Third Level (Tertiary Prevention): develops on individuals with behavioral manifestations (students with behavioral disorders). It is identified with rehabilitation, which is considered as the system of actions that is carried out with the objective of achieving an optimal physical, mental and / or social functional level in a person with a disability.
Fourth Level (Quaternary Prevention): it is carried out on people with more complex manifestations, with the aim of reinserting them back into society as a useful being. It is based on the equalization of opportunities, considering this the process by which the general system of society (health, culture, housing, transportation, social and health services, education, work, including sports and recreation facilities), is makes it accessible to everyone (Castillo del Risco et al., 2013).
From this perspective, it comes with finding ways to improve the prevention of indiscipline of the students to the lowest possible level, in this case a second level of prevention. With the intervention in this process for each agency, organization and community workers, from their missions, taking an interactive and multifactorial action that, in an integrated manner, will impact on the students who break those school duties do not become in students with a diagnosis of conduct disorder.
In the current article, the study of the problem is exposed: How to prevent the worsening of indiscipline in students from the province of Pinar de Rio? It has as objective: socialize a strategy to prevent aggravating indiscipline in students from the province of Pinar de Rio.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A explanatory descriptive study applied Pinar del Rio is presented, for which it is taken from a total enrollment of 70,950 students, a sample of 421 schoolchildren with manifestations of indiscipline (violators homework) selected intentionally, which passed through the education system of the 2017-2018 and 2018-2019 academic years; as well as 389 teachers and 412 families of the students in the sample. The study evaluates the effectiveness of a strategy to prevent the aggravation of indiscipline in students in the 11 municipalities of the Pinar del Río province.
In its development, different research methods are used, among which are theoretical methods; empirical and statistical.
The theoretical methods used were:
The document analysis method for the study of documents on the preventive work of teachers who attend students with manifestations of indiscipline (noncompliant with school duties) and their families.
In addition, the systemic approach method was used, which provided the general orientation for the elaboration of a strategy to prevent the aggravation of indiscipline in students from the province of Pinar del Río.
The analysis-synthesis and induction-deduction procedures were used in conjunction with the empirical methods, both in the verification of the problem and in the interpretation of the information collected during the study carried out.
The empirical methods used were:
The interview, the observation and the case study: to know the characteristics of the students, who present indiscipline, manifested in non-fulfillment of the school duties, at first, and their evolution after the strategy is applied.
RESULTS
The psycho pedagogical diagnosis is the fundamental tool that teachers have to characterize students and draw intervention strategies for their educational attention, taking into account their needs and potentialities, which is why it must be the domain of managers and teachers, who with their daily work need to use these processes. Through them, a basic knowledge is sought and built, to promote the course of its development; this intervention will continue to be controlled by moments of evaluation and diagnosis.
The study began taking into account the status of the indicators in the fulfillment of school duties, at the end of the 2017-2018 school year.
In the month of November of the 2017-2018 academic years, a total of 421 students who did not comply with their homework were identified, representing 0.59 % of the total daytime enrollment (70,950). Of this universe, 75 (17.8 %) failed to meet more than one indicator.
The indicator in which the largest number of students was concentrated was number 4 (student behavior) 232, representing 55.1 % of the total; with the highest incidence in the Basic Secondary education levels with 168 and ETP with 118. In indicator number 1 (school attendance and punctuality) there were 148 students, which represented 35.1 % of the total; with higher incidence in educational levels ETP 69 and Basic Secondary with 52. In the indicator number 5 (correct use of the school uniform) 61 students were controlled (14.4 % ) with higher incidence in ETP 43 (Table 1) .
Table 1- Survey of students who fail to comply with school duties for the 2017-2018 academic year
No |
Education level |
Total of |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
Attended in more than one |
1 |
Primary |
116 |
19 |
4 |
5 |
95 |
2 |
6 |
9 |
2 |
Special |
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
3 |
Basic Secondary |
168 |
52 |
14 |
15 |
105 |
9 |
|
2. 3 |
4 |
Technical and Professional |
118 |
69 |
12 |
11 |
29 |
43 |
6 |
42 |
5 |
Pre-university |
18 |
8 |
2 |
|
2 |
7 |
|
1 |
|
TOTAL |
421 |
148 |
32 |
31 |
232 |
61 |
12 |
75 |
Legend
Indicators:
1. School attendance and punctuality
2. Continuity and permanence in the National Education System
3. Completion of school assignments
4. Student behavior
5. Correct use of the uniform
6. Care of the material aids (BME ) , the teaching aids of V leg (BMV) and school facility
The 389 teachers working with students who have manifestations of indiscipline, mainly those in training, graduates and reintegrated constituted interest variables. Analysis of the results showed that teachers with more than five years old experience 224 (57.5 %) are the largest per cent working with these students (Table 2) .
Main causes that hinder the integral attention of teachers to students:
- Non-use of personalized diagnosis as a work tool.
- Poor command of the characteristics of the evolutionary development of the students with whom they work.
- Difficulties in directing the teaching - educational process taking into account the levels of assimilation.
- Difficulties in attending to individual differences.
Table 2 - Origin of teachers who attend students who fail to fulfill school duties
Educations |
Students who fail to comply with school duties |
Teachers who serve them |
||||
Teachers in training |
Recently graduated teachers |
Experienced teachers |
Reincorporated teachers |
Total teachers |
||
Primary |
116 |
21 |
25 |
62 |
8 |
116 |
Special |
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
Basic Secondary |
168 |
42 |
3. 4 |
71 |
6 |
153 |
Technical and Professional |
118 |
6 |
5 |
81 |
11 |
103 |
Pre-university |
18 |
4 |
3 |
9 |
|
16 |
TOTAL |
421 |
73 |
67 |
224 |
25 |
389 |
The 412 family studied is an essential element for guide preventive work and developer, so knowing its characteristics is essential , both to determine the causes of student demonstrations as the work of guidance on work To make. The inadequate educational methods used by the family to exercise control over their children is the characteristic that is most evident in the study that is carried out. For this item ,207 are reported , accounting for 50.2 %, followed by 103 imbalances in the emotional situation with 25 %, overprotection with 17.2 % and inadequate moral behavior with 15.7 %, among others. All these characteristics of the family environment reinforce negative behavioral patterns in the development of the personality of students. See results in table below (Table 3).
Table 3 - Characteristics of the family of the students in the sample under study.
Educations |
Students who fail to comply with school duties |
Main characteristics of the family |
||||||
IME |
DRI |
CMI |
DSE |
V |
S |
Total families |
||
Primary |
116 |
85 |
7 |
2. 3 |
14 |
4 |
39 |
112 |
Special |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
Basic Secondary |
168 |
48 |
21 |
26 |
64 |
12 |
27 |
165 |
Technical and Professional |
118 |
72 |
5 |
12 |
2. 3 |
24 |
2 |
116 |
Pre-university |
18 |
1 |
6 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
18 |
TOTAL |
421 |
207 |
39 |
65 |
103 |
42 |
71 |
412 |
Legend
IME: Unsuitable Educational methods
DRI: Difficulties in Interpersonal Relationships
CMI: Inadecuated Moral Behavior.
DSE misadjusted Emotional Situation
V: Violence between members of the family
S: Overprotection
Based on these results, a strategy with a multifactorial and multidimensional nature is drawn up, which affects students who fail to fulfill school duties, teachers who attend them and their families.
Strategies to prevent the worsening of indiscipline among students in the province of Pinar de Rio
Many of the things that we need are waiting: the Child does not.
He's making his bones right now, raising his blood and
Rehearsing his senses. You cannot answer him: "Tomorrow"
He is called "Now" ...
Mistral (cited by Rubilar, 2017)
Fundaments of strategy
The understanding of the prevention of Behavioral Disorders starts from the assessment of important criteria as referents, about the development of personality and behavior. Man, as a social being, expresses the characteristics of his personality through the behavior he assumes in all situations of daily life; In the case of students inserted in the educational system, one way of manifesting it is with the fulfillment of their school duties, not fulfilling them is interpreted from this prism as alterations in their behavior, which influences their formation and development. Obviously, from Dialectic materialistic foundation we start from a clear criterion on the concept of development.
The analysis of the category of development, from the elaborated theory by Vygotsky (1989), has been essential to fundament this study. The social determinism of the psychic development is a thesis based on the philosophical premise that man is a social being by nature, a product of society and a subject of social relations.
The special combination of internal processes and the external conditions that occur in each stage of human development determines the dynamics of psychic development during the evolutionary period, while the new psychological formations that emerge towards the end of each stage cause the social development situation .
From the first days of life, objective conditions exist in the child that constitutes the basis and the driving force of all psychic development. The level reached by an individual in it (from childhood to adulthood) depends on the culture that has the social group in which it operates, of the historical moment in general and of the particular group.
From this thesis, the interpretation is made of the relationship between biological and social; to the pose that there are natural psychological functions that have a biological origin and are distinguished from the higher functions that originate in social relations is recognized.
Vigotsky (1989) formula, moreover, the genetics fundamental law of development, from which it is appreciated that all psychological function exists at the least two levels: first social, inter psychological or communication and the second, in the plane psychological individual or intra psychological and refers that the process occurs through the internalization mechanism, where mediators play a fundamental role.
It is assumed in this work the essential notion of the historical - cultural focus Declared by Vigotsky (1989), based on the fundamental genetic law of development: the ZPD, which refers to the distance average between the actual level of development, determined by the actual ability to independently solve a problem, and the potential level of development, determined through solving a problem under the guidance of an adult or under the collaboration of another capable partner. It is clear that to apply aid levels also involves using different modalities to bring about a leap in development, It is to say the change.
This change takes place to the extent that participation guided by demonstrations is achieved; later with supportive actions and finally , with guidance, it is achieved that he can do it on his own; This enables the necessary independence to be able to help others and that the adequate establishment of the emotional climate favors interpersonal relationships and enhances development.
The affective development takes place in a similar way to the moments proposed by Vigotsky (1989), in terms of the development of higher psychic functions, hence the necessary integration between the cognitive and the affective in qualitatively new formations; precisely constituted of a new level of human development: the personality.
It is also important to point out that motivations based on experiences are linked with all emotional potential to cognitive operations that closely shape the personality. (Bermúdez, Saínz, Barrera & Pérez, 2017).
From this understanding, the personality is then a stable and systemic organization of the psychological contents and functions that characterize the integral expression of the subject in its regulatory and self- regulatory relationship of behavior.
It is formed as an individual reflection of the set of relationships and social conditions of life, so it is a process of development conditioned historically and socially, where social communication also plays a decisive role in the activity.
The regulatory and self- regulatory function of the personality allows the subject to direct their own psychic development (self-regulation), to harmonious condition and stable forms of orientation and execution of the activity that takes into account internal and external influences and reflects the level of development of the unit of the affective and the cognitive, according to what was proposed by González Rey (cited by Bermúdez, R. et al, 2017).
These functions allow the subject to orient himself to act, to carry out his activity realizing what he is doing and to experience and feel that the regulation he makes of his activity is what leads him to the result.
The behavior of the human being implies as a core aspect its relationship with moral norms, with the values of society, so it can be said that it has a social, ideological and moral content.
The strategy addressed is based from the historical cultural approach, It is enrolled in the second level of prevention for the attention to indiscipline expressed in no observance of students homework inserted in the education system in the province of Pinar del Rio in order, firstly, to prevent them becoming students diagnosed with conduct disorders and , as a result, to reach eventually in social indiscipline (Figure 1).
Objective: To better preventive community work from the work of School Councils of the group of preventive work, fostering joint action with organisms and organizations dealing with students who commit indiscipline manifesting breach of the school duties, to avoid the aggravation of their behavior that generates a diagnosis of conduct disorder and guarantees their comprehensive training, a healthy and useful life.
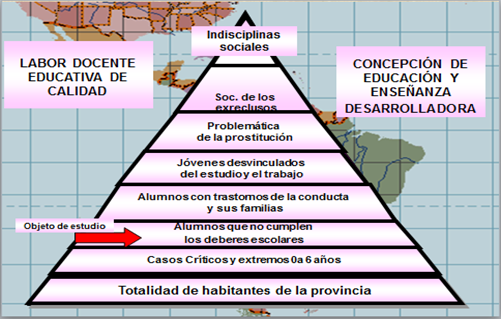
Fig. 1- Pyramid of preventive work (Bravo, M. Personal communication: Topic given at the Provincial Seminary for educators in Pinar del Río, May 2016)
Principles that support the strategy. Nieves (cited by Castillo del Risco et al., 2013):
1. Early identification and early attention to risk groups: It is based on the need to initiate preventive actions as early as possible as an essential condition to avoid the emergence, development and / or stability of what you want to avoid, correct or compensate.
2. Principle of the systemic nature of the intervention and follow - up: define the need to develop preventive work and control efficiency through a coordinated set of actions that are performed by different actors, agencies and integrated organizations making process joint decision-making.
3. Principle of ecological approach to prevention: establish the importance of the approach, assessment and attention to difficulties, taking into account the place of the environment in its emergence and development, so that preventive go aimed at achieving transformations of the school, family, and community environment where the minor is inserted, with a view to perfecting the system of influences.
4. Principle of dialogic nature of the decision and preventive action: to alert on the need for decisions and actions that characterize the preventive actions, have their basis in a constructive, participative relation and joint responsibility of all the factors that make up the system of influences.
Based on the principles outlined above and taking into account the fundamental causes that are causing said problem, the following strategic objectives are proposed:
1. To improve the training and improvement of teaching staff based on the systematic and permanent improvement of cadres and teachers to guarantee the quality of the educational management process and the educational teaching process.
2. Revolutionise the educational system, perfecting the educational work of teachers and the family, from the continuous elevation of their exemplary nature and their ability to form values in healthy, cultured and deeply revolutionary children, adolescents and young people.
3. To achieve that the entire population - with emphasis on children, adolescents and young people, based on the development of their capacities, convert the opportunities that the revolution offers them, into true possibilities of acquiring a comprehensive general culture and full social integration.
Strategic actions to develop:
AREAS |
ACTIONS TO BE DEVELOPED |
PARTICIPANTS |
|
|
Management and methodological structure of the Provincial Directorate of Education (DPE) |
|
DPE, FMC, CDR, INDER, OPJM, FEEM, ACRC |
|
|
DPE with the participation of the FMC |
|
|
DP E, agencies and organizations |
|
|
Subheads, principal of departments and teaching methodologists |
|
|
Deputy directors, heads of departments and teaching methodologists |
|
|
Subheads, heads of departments and teaching methodologists |
|
|
Subheads, head of departments and teaching methodologists |
|
|
Members of the Board of Directors |
|
|
Subheads, head of departments and methodologists. |
|
|
President of the Commission subject of History, head of departments, methodologists of Primary and Judges. |
|
|
Subheads heads of departments and methodologists |
|
|
Subheads heads of departments and Methodologists and Art Education Methodologist |
|
|
Subheads, heads of departments and methodologists |
|
2. Functioning of the School Councils |
|
DPE, FMC, CDR, INDER, OPJM, FEEM, ACRC |
|
Members of the selected councils |
|
|
Subheads, heads of departments and methodologists. |
|
|
General Deputy , sub directors of Educations, heads of departments and methodologists of DPE |
|
3 . Functioning of the preventive working group |
|
General Sub director of school health, CDO, inspection, representation educations, organs, agencies and organizations |
Legend
DPE: Provincial Directorate of Education
FMC: Cuban Federation Women
CDR: Committee for the Defense of the Revolution
INDER: National Sports Institute
OPJM: José Martí Pioneers Organization
FEEM: Federation of Middle School Students
ACRC: Bowyers Association of Cuban Revolution
CAM: Council of Attention to Minor
ANAP: National Small Agricultures Association
CDO: Center of Diagnosis and Guidance
EFI: Integral Formation Schools
MINSAP: Ministry of Public Health
MINED: Ministry of Education
MINCULT: Ministry of Culture
MTSS: Ministry of Work and Social Security
MININT: Ministry of the Interior
Form of implementation of the strategy
For the implementation of the strategy it is proposed:
In particular, the articulation in the work system of the Provincial Directorate of Education must be achieved:
Strategy evaluation form
Actions for the evaluation system of the provincial management strategy and municipal education directorates
• Analyze the actions that have been derived from the diagnosis for preventive work in particular and in the teaching - learning process generally in the municipalities (all educations).
• Participation of the Educations in monthly meetings convened by the group of preventive work.
• To confirm the participation of the municipal structure in the meetings of the councils of school from planning (all educations).
• Knowledge that is possessed in the territory about incidents that occurred in the centers and especially in relation to the drug issue, as well as the attention and control of the centers where situations of this type are repeated and the participation of students controlled as noncompliant of the school homework.
• Projections of the pre university Educations and ETP in relation to the prevention of indiscipline, consumption of substances harmful to health and other inappropriate practices of students, both inside and outside the centers.
In educational centers:
• Results of the strategies made from the characterization of students and teaching center:
- Implemented actions aimed at the areas of knowledge and behavior of all students in all contexts of action and their effectiveness.
- Actions that have been derived from the characterization for preventive work in particular and in the teaching - educational process in general at school.
• Process attention of students in meeting the homework and functioning of the Board of School:
- Control exercised to the attention of students who do not fulfill school duties and their evolution. Test results in psycho pedagogic commissions and the Council of school.
- Check in home visits the attention given by agencies and organizations to students who do not fulfill their homework.
- Relationship between the incidents that occur in the centers with the schoolchildren controlled as noncompliant with school duties.
- Relationship between the incidents that occur in the centers with the schoolchildren controlled as noncompliant with school duties.
- Development of monthly meetings of the school councils. Content and quality of the topics covered. Participation of all members, emphasizing the representation of the FMC, CDR, the representative of Preventive Work of the DME before the Popular Council. Role of the president. Visits made by the structures to the meetings.
- Mastery by the schools of the students with individualized measures by the Council for Attention to Minors for Education or the MININT, case studies to know causes and conditions that originated the conduct disorder (reflections on failures in educational work).
- Disclosure is done with regard to the bad habit of smoking and to alcoholism. Preparation of the teaching group.
- Curricular output of these aspects with the students.
- Specify the control of medications in those territories with internal centers and of workers and students who consume psychotropic drugs.
Once the strategy is implemented, it managed to decrease the number of students who show worsening manifestations of indiscipline in the province of Pinar de Rio ( Table 4).
Table 4 - Evolution of students who fail to fulfill their homework once the proposed strategy is applied
No |
Education level |
Total of students who breach |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
Cases solved |
1 |
Primary |
116 |
19 |
4 |
5 |
95 |
2 |
6 |
64 |
2 |
Special |
one |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
Basic Secondary |
168 |
52 |
14 |
15 |
105 |
9 |
0 |
109 |
4 |
Technical and Professional |
118 |
69 |
12 |
11 |
29 |
43 |
6 |
82 |
6 |
Pre-university |
18 |
8 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
7 |
0 |
12 |
|
TOTAL |
421 |
148 |
32 |
31 |
232 |
61 |
12 |
268 |
Legend
Indicators:
1. School attendance and punctuality
2. Continuity and permanence in the National Education System
3. Fulfillness of school assignments
4. Student behavior
5. Correct use of the uniform
6. Caring for the BME , the BMV and the school installations
DISCUSSION
Preventive work strategies were traditionally designed within each educational level. In the preventive work groups emerge in the educational system of the MINED, strategies are generated with an interactive and multifactorial character; in this way, the educational levels are involved in its implementation, which encourages the participation of community agencies, organizations and agencies in the education of our students. Example: Table 4.
The diagnosis made to verify the existence of the problem studied on how to prevent aggravating indiscipline in students from the province of Pinar de Rio, corroborated that no matter that in the last three years has decreased the number of students who show indiscipline in the breach of homework that affect are continuity and remain in the National Education system and behavior of the students. Examples: table 1 and table 4.
It has been shown that the root causes in this situation were given by the absence of a strategy that favors the use the diagnosis and, consequently, a push consistent among all the factors involved in the development of the educational work; the lack of legal preparation of cadres, methodologists and teachers; the analysis in the technical and management bodies on the subject that does not always propitiate the process of making timely and inclusive decisions for the attention to the students from the first vestiges of manifestations of indiscipline they present; In this process, effective integration between education and the Center for Diagnosis and Orientation (CDO) is not achieved .
The proposed strategy to prevent the aggravation of indiscipline in students, with an interactive and multifactorial nuance, is based from a developmental perspective on the Cuban experience on preventive work, which makes it viable for the fulfillment of the proposed objective and feasible from its insertion in the Labor System of the Provincial Directorate of Education in Pinar del Río.
Provincial Directorate of Education has within its services ensured the development of educational work quality, for which it instruments the substantive process: preventive and Community work and developing actions that help prevent manifestations of indiscipline of students.
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCES
Almaguer, Y.R. & Almaguer, S. (2017) Acciones para la formación del valor responsabilidad en adolescentes con trastornos de conducta. Revista Educación y Sociedad. 15(3), pp. 49-61.
Bermúdez, R., Saínz, L., Barrera, L.M. & Pérez, L.M. (2017) La personalidad: Diagnóstico de su desarrollo. (Libro Online). Las Tunas: Universidad de Las Tunas. pp. 31-38. Recuperado de http://roa.ult.edu.cu/bitstream/123456789/3733.
Castillo del Risco, Y., Gómez, A.L., Núñez, O.L., Gómez, E., Olica, B., & De Armas, E. (2013) Carácter preventivo en la atención a las dificultades en el aprendizaje en niños con diagnóstico de retardo en el desarrollo psíquico. EFDeportes.com, Revista Digital. Buenos Aires, 18(185). Recuperado de https://www.efdeportes.com/efd184/caracter-preventivo-en-retardo-en-el -desarrollo.html
Ferrer, D.M., Martín, R. & Suz, M.A. (2019) Niñez, familia y violencia. Miradas en la región central del país, desde diferentes perspectivas. En Jiménez, A., & Sarduy, Y.B. (Ed). Pensar en las infancias cubanas: coordenadas socioculturales (pp. 119). La Habana: Instituto Cubano de Investigación Cultural Juan Marinello. Recuperado de http://biblioteca.clacso.org/Cuba/cidcc /20200304054900/2.pdf
García, I.C., & Tamayo, J. (2018) Las políticas educativas inclusivas en Cuba. Revista Científico Metodológica Varona, Edición especial, (Online) 66 supl.1. Recuperado de http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1992-8238201800010...
PCC. (2017). Documentos 7mo. Congreso del Partido aprobados por el III Pleno del Comité Central del PCC el 18 de mayo de 2017 y respaldados por la Asamblea Nacional del Poder Popular el 1 de junio de 2017. Compendio. La Habana: Comité Central del PCC
Peña, Y., Garcés, J.E., & López, S.A. (2017) La prevención de trastornos de conducta desde la Educación Física escolar. OLIMPIA. Revista de la Facultad de Cultura Física de la Universidad de Granma, 14(45), Edición especial. pp. 297-311
Romo M.C., Ramos A., & Velázquez P.Z. (2017) Análisis de las estrategias docentes para promover la convivencia y disciplina en el nivel de educación preescolar. Educación, 26(51):35-54. Recuperado de http://www.scielo.org.pe/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1019 -94032017...
Rubilar L. (2017) Gabriela Mistral y el imaginario pedagógico chileno. Memoria Chilena, artículos para el bicentenario pp.13 Recuperado de http://www.memoriachilena.gob.cl/602/articles-123217_recurso_2.pdf
Valle, A., Aguilartes, Y., & Rodríguez, Y. (2016) Plan de acciones para prevenir indisciplinas sociales en jóvenes. EduSol, 16(54), ene.-mar., Universidad de Guantánamo, Cuba, pp. 11-24.
Vigotsky, L.S. (1989) Fundamentos de Defectología. Obras completas tomo V. Editorial Pueblo y Educación: La Habana.
Conflict of interest:
Authors declare not to have any conflict of interest.
Authors´ Contribution:
Authors participated in the writting process of this article and in the analysis of documents.
![]()
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) Marisol Bravo Salvador