
Mendive. Revista de Educación, april-june 2019; 17(2):264-275 
Translated from the original in Spanish
System of evaluation of impacts of the Master in Management
Sistema de evaluación de impactos de la Maestría en Dirección
Tania Vargas Fernández1
1 University of Pinar del Río "Hermanos Saíz Montes de Oca». Faculty of Economic and Business Sciences. Center for Studies of Management, Local Development, Tourism and Cooperativism (CE-GESTA). Pinar del Río, Cuba. Email: tvargas@upr.edu.cu
Received: February 2nd, 2019.
Approved: April 1st, 2019.
ABSTRACT
Master's Degree in Management, coordinated by the Center of Studies of Management, Local Development, Tourism and Cooperativism of the University of Pinar del Río, is aimed at enhancing the search for efficiency and effectiveness in the results of organizations and their effect on the sustainable development of the territory. It intends to propitiate the systematic increase in the capacity of change of the organizations and of the territory, in correspondence with the conditions that the economic and social development of the country demands. The curriculum of the Master´s degree is designed on the base of a system of objectives focused towards the students´ development skills, on the sake of scientific and technical problems linked to the sphere of the management. However, this Program lacks an own mechanism to evaluate its impact. For this reason, the purpose of this work is to design an impact evaluation system for the Master's Degree in Management, which contributes to the continuous improvement of the Program's quality. There were used methods from theoretical level as, historical-logical, systemic approach and modeling, with the aid of the documentary analysis technique, as well as the procedures analysis-synthesis and induction-deduction. All of them based on the Dialectic Materialist method fundamentally in the study of diverse models, systems and methodologies of impacts evaluation that served as theoretical-methodological referents, what allowed to determine their main contributions and limitations,as a base for the carried out proposal. The proposed system has nine components, which as a whole will contribute to the continuous improvement of the program´s quality.
Keywords: evaluation; evaluation of impact; impact; system.
RESUMEN
La Maestría en Dirección, coordinada por el Centro de Estudios de Dirección, Desarrollo Local, Turismo y Cooperativismo de la Universidad de Pinar del Río, está dirigida a potenciar la búsqueda de eficiencia, eficacia y efectividad en los resultados de las organizaciones y su efecto en el desarrollo sostenible del territorio. Con la misma, se pretende propiciar el aumento sistemático en la capacidad de cambio de las organizaciones y del territorio, en correspondencia con las condiciones que demanda el desarrollo económico y social del país. El currículo de la Maestría está diseñado sobre la base de un sistema de objetivos enfocados hacia el desarrollo de habilidades en los maestrantes, en función de la solución de problemas científicos y técnicos vinculados a la esfera de la gestión. Sin embargo, este Programa carece de un mecanismo propio que permita evaluar su impacto. Por tal razón, el propósito de este trabajo es elaborar un sistema de evaluación de impactos de la Maestría en Dirección, que contribuya a la mejora continua de la calidad del programa. Se emplearon los métodos de nivel teórico: histórico lógico, sistémico y de modelación con el apoyo de las técnicas del análisis de documentos y los procedimientos de análisis y síntesis e inducción y deducción. Todo ello sustentado por el método materialista dialéctico, para el estudio de diversos modelos, sistemas y metodologías de evaluación de impactos que sirvieron como referentes teórico-metodológicos, lo que permitió determinar sus principales aportes y limitaciones, como base para la propuesta realizada. El sistema propuesto está conformado por nueve componentes, los cuales en su conjunto contribuirán a la mejora continua de la calidad del Programa en cuestión.
Palabras clave: evaluación; evaluación de impacto; impacto; sistema.
INTRODUCTION
The Master in Management program of the University of Pinar del Río is designed for the development of professionals in the fields of business, public and cooperative management, as well as institutions of higher education and science, and is intended strengthen the search for efficiency, efficacy and effectiveness in the results of organizations and their effect on the sustainable development of the territory.
The knowledge and skills provided by the program make graduates agents that foster and influence the systematic increase in the capacity of change of the organization where they work, in correspondence with the conditions demanded by the economic and social development of the country.
From this perspective, it is increasingly necessary for organizations to develop their management systems according to the demands of the socio-economic environment where they are located, for which the training of human resources, with theoretical and practical knowledge in these topics is of an essential importance (Sánchez, Laguna & Téllez, 2018).
As part of the investigative process that gave rise to this work, it was detected that, regardless of whether the Ministry of Higher Education (MES) through the National Accreditation Board, establishes a System of Evaluation and Accreditation of Higher Education (SEAES) , within which several subsystems are integrated, such as the SEA-M (Master Evaluation and Accreditation Subsystem) and that there are other investigations that address the issue in question; The Academic Master's Program in Management at the University of Pinar del Río lacks a mechanism that specifies its objectives and needs with a view to assessing its impact on the different actors that are part of the training process.
The aforementioned considerations led to the approach of the scientific problem of research: how to contribute to the improvement of the quality of the Academic Master's Program in Management, belonging to the University of Pinar del Río?
The evaluation of the Program will be aimed at achieving quality management to meet the needs of trainees, employers and society in general. It will rely on self-assessments, the realization of adjustments and continuous improvement, external evaluation and quality accreditation.
There are several authors who have proposed models, systems and methodologies related to the subject under study. Various national and international references, among which were analyzed: mo Delo(Kirkpatrick, DL & Kirkpatrick, J. D, 2009), model Phillips (1990), model (Wade, 1999), model (Pineda, 2000), guide for the evaluation of the impact of training (Billorou, Pacheco & Vargas, 2011), System of Evaluation and Accreditation of Higher Education (MES, 2018), instrument proposed by (Ramos et al. 2016), criteria for the evaluation of the academic impact of Master's Programs, of (Mestre, 2016), methodological strategy of (Lara et al. 2018), the methodology to evaluate the impact on the local development of (Sánchez et al. 2018), among others.
The objective of this work is to develop an impact evaluation system for the Master in Management, which contributes to the continuous improvement of the quality of the Program.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In the development of the research the theoretical level methods were used: logical, systemic and modeling history with the support of the techniques of document analysis and the procedures of analysis and synthesis and induction and deduction. All this supported by the dialectical materialist method.
The main contributions and limitations of models, systems and methodologies that predate the one proposed in the work and with the use of the systemic and modeling method were determined, the impact evaluation system of the Master in Management was proposed, establishing its components and internal relationships
For the implementation of the system, the application of techniques is proposed, such as surveys and interviews with students, graduates, cloisters, employers and managers of the area to which the Master's Program in Management belongs; which will allow obtaining information necessary to take action regarding its continuous improvement.
The type of research developed was descriptive, while the impact assessment process and its components were analyzed. On the other hand, this research was also considered as a technological or fundamentally oriented development, because it was aimed at acquiring new knowledge oriented to a well-defined practical objective and obtaining a new system on a scale that allows its subsequent generalization.
RESULTS
Taking into account that a system is the set of interrelated elements or interacting (National Bureau of Standards, 2015) and the impact evaluation of the educational process is the process that measures the degree of importance that the application of the evaluable object in the specific socioeconomic environment in order to assess its effect on objects and asure applied improved selection of new objects of evaluation(Añorga, 2014); The Impact Assessment System of the Master in Management (SEI-MD), is based on the need to achieve better quality management of the Program evaluating its impact on the socio-economic environment where the actors involved, through employment of different instruments that contribute to its continuous improvement.
The evaluation of the impact of projects and programs is a complex task, since measuring the impact is trying to determine what has been achieved, which is generally difficult when it comes to evaluate qualitative changes (Lara, Navales & Bravo, 2018).
Based on the elements outlined above, an impact evaluation system of the Master in Management is proposed, composed of the following components:
1. Object
2. Objective
3. Principles
4. Premises
5. Actors involved. Functions
6. Graphical representation
7. Explanation of its elements and relationships
8. Forms of instrumentation
9. Quality pattern
A detailed explanation of these components is given below:
1. Object
Process of evaluation of the impact of the Master's Program in Management
2. Objective
Evaluate the correspondence between the objectives of the Master's Program in Management and the results achieved by the participants, by systematically measuring the impact of the training on them and their contexts of action, in relation to the established quality requirements.
3. Principles: participatory, transparent, reflective and ethical
4. Premises
5. Actors involved. Functions
The roles of these actors are reflected in different documents, such as regulations, standards, manuals, instructions and the interested parties can consult resolutions at different levels and that.
Only the functions of the self-assessment commission, created for the purposes of the Impact Assessment System of the Master's Program in Management (SEI-MD), will be detailed.
Functions of the Self-Evaluation Commission:
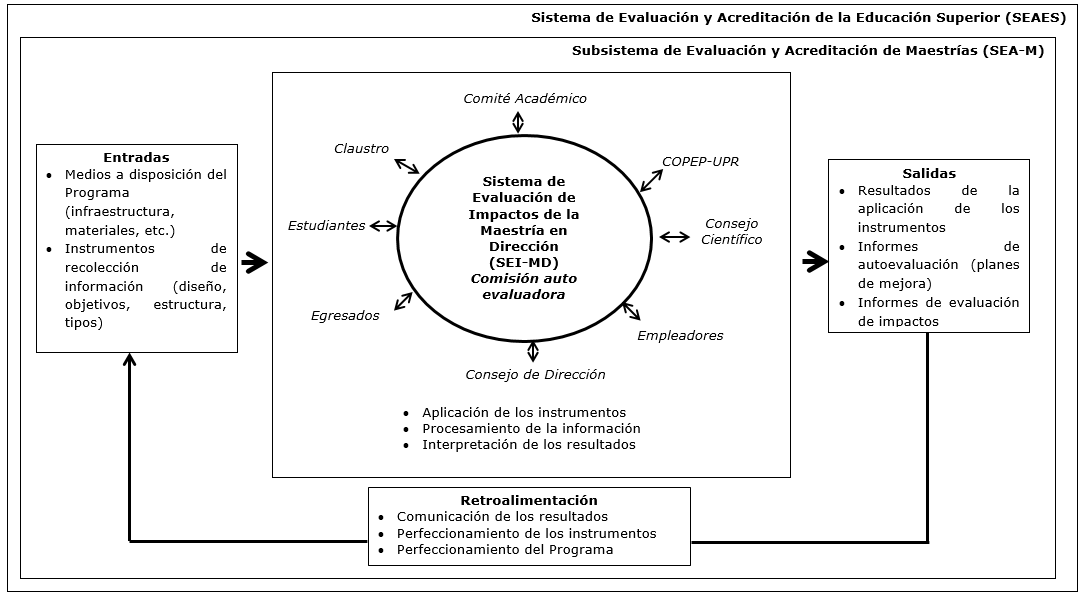
Fig. 1 - Impact Assessment System of the Master in Management (SEI-MD)
7. Explanation of its elements and relationships
The self-evaluation is an integral process, oriented to the determination of the state, the operation and the projection of the Program in correspondence with the predetermined one, to the obtaining of new knowledge on the object that is evaluated to emit judgments that contribute to strengthen the process and correct the weaknesses
Its main product is the improvement plan and the elevation of the culture of quality, but for the realization of a self-assessment report at the end of each edition, is necessary to systematically evaluate the progress of the Program and correct the deviations that may arise in time.
It is in this systematic evaluation that the proposed system focuses its attention, although it does not exclude the self-assessment at the end of each edition, as established by the SEAES.
The SEI-MD is a subsystem of the SEA-M, which in turn in a subsystem of the SEAES and has as inputs the means available to the Program, that is, the infrastructure and materials that support the successful execution of the program. , as well as the instruments for collecting information, when defining their design, objectives, structure and types.
In the impact assessment, the actors defined in previous sections participate, which are closely related to the process in question, being part of it as a population under study or as decision makers that manage, coordinate or supervise the process. The role of the self-assessment commission is essential, while it will be in charge of actually carrying out the proposed system.
As part of this process, the application of the instruments, the processing of the information and the interpretation of the results will be carried out; this will lead as outputs of the system to the realization of the results and the presentation of the relevant self-assessment reports, with their respective improvement plans. At the end of each edition, as established by SEAES, a self-assessment report will be made.
In addition, it is proposed to carry out a summary report of impact evaluation with the following structure: cover, introduction, main results of the edition (qualitative and quantitative), explanation of the instruments used to assess the impact and of the actors involved, results of the analysis derived from the application of the instruments, improvement proposals (instruments, program) and conclusions.
The instruments to be applied are part of the systematic evaluation referred to above, at the same time, the information obtained from its processing serves as a reference for the preparation of the self-assessment report at the end of the Program duration.
Close the system, the feedback process, with the consequent communication of the results (partial and final) to the relevant actors, It is to say: members of the Academic Committee, Board of Directors, Branch Scientific Council of Economic Sciences and COPEP-UPR, in order to take corrective and / or preventive actions that allow the continuous improvement of the Master's Program.
From a general assessment, Añorga (as cited in Rodríguez, Mena & Lazo, 2017), assigns a high importance to the evaluation as an essential element of feedback.
The feedback will allow, the improvement of the evaluation instruments, so that they can be adapted to the particularities of the population under study and to the information needs of the Program for its continuous improvement. Likewise, those changes or adjustments necessary for its improvement must be assessed based on the results obtained and in accordance with the superior category of quality accreditation that the Program possesses.
The evaluation of the tax impact to give feedback to the system and as a consequence to increase its quality and increase its impact on the economic and social development of the territory.
8. Forms of instrumentation
To plan and monitor the academic and research activities provided for in the Program and thus be able to determine its impact, this process is divided into three fundamental moments: before, during and after training; taking into account the use of techniques and actions, such as surveys, interviews, documentary review, group work, visits to entities, exchanges of experiences, among others.
In the "before training" stage, a forecast of the possible impact that it will have is established, through a set of elements or indicators related to the socioeconomic context, the target population, the problems and needs to overcome, the necessary inputs and the level of motivation to learn.
The second stage: «during the training», is the moment where all the actions included in the schedule are executed and its effectiveness is evaluated, taking into account its correspondence with the needs and interests of those involved in the process. At this stage, instruments will be applied to assess student satisfaction with each course taught.
Finally, the "after training" stage allows you to assess whether the proposed objectives were met and adopt any adjustment or adaptation for future editions. It is checked if the indicators established in the first stage were modified, if the expectations of those involved were met and if there was transfer of knowledge to other managers and workers of the entities and organizations involved in the process.
This last stage will consist of two phases: immediate and mediate. In the immediate phase, the level of student satisfaction with the Master's program will be assessed at the end of the edition. Instruments will also be applied, as part of the mediated phase, at the end of one year after the end of the edition, so that the degree of application of what has been learned in their work contexts can be evaluated. The foregoing does not imply that in that period no instruments are applied that allow the Program to be readjusted. In fact, in that period another edition will already be in execution and therefore, tools will be applied for that purpose.
Table 1 summarizes the levels and stages that will be taken into account as part of the SEI-MD.
Table 1 - Levels and stages for the evaluation of the impact of the Master's Program in Management.
Stages |
||
Levels |
During the training process |
At the end of the Program |
1. Reaction: |
It evaluates the satisfac tion of the study teas with each course taught. |
The tisfaction of graduates and their employers with respect to the Program is evaluated. |
2. Learning: |
It evaluates the learned zaje of study tes taught in each course. |
It is evaluated whether the graduates have acquired the skills planned in the Program, taking into account the criteria of the graduates and their employers. |
3. Impact: |
It is assessed whether graduates have transferred the knowledge learned in each course to their work context. |
It is evaluated if the graduates have transferred the knowledge received to their daily work and how the training received has an impact on their professional performance and organization. |
Source: Adapted from Ramos, Meizoso & Guerra (2016)
It is proposed to apply the following instruments and actions for the evaluation of the impact of the Master's Program in Management:
Students:
Cloister:
Directors of the area:
Graduates:
Employers:
In the search for the operationalization of the program's impact evaluation process, the set of indicators proposed in the evaluation guide of the SEA-M will be taken into account, which symbolize qualitatively or quantitatively relevant aspects in which strengths and weaknesses the indicators are broken down into evaluation criteria that together characterize them.
9. Quality pattern
Corresponding to what is stated in the SEAES Ministry of Higher Education (MES, 2018), the quality pattern is identified with an ideal model to which the quality of the object evaluated should approximate. It defines the "must be" of Higher Education programs or Institutions, understanding quality as the conjunction of academic excellence and social relevance given by the purposes of the development of the Cuban historical, sociocultural and economic project. It constitutes the description of a set of stable qualities expressed in variables and indicators in the different SEAES subsystems.
To determine the extent to which a Master's Program meets the corresponding quality standards, five variables are established (MES, 2018):
1. Relevance and social impact
2. Cloister
3. Students
4. Infrastructure
5. Curriculum
It is not the interest of the proposed system to resume what the SEAES establishes for the self-evaluation of a postgraduate academic program; although the SEI-MD would not be complete if it does not take into account the proposed Quality Pattern as part of the SEA-M that serves as a reference to make the self-assessment report at the end of each edition, as the basis for the opening of a new edition and for the request of the external evaluation to the competent organs.
For this reason, the content of the SEAES and the SEA-M subsystem will constitute a mandatory reference for the SEI-MD, say quality standard, evaluation guide and master's implementation manual, as well as the models and annexes required for the preparation of the program's self-evaluation report.
DISCUSSION
For the proposal of the Impact Assessment System of the Master in Management, several models, systems and methodologies related to the topic of analysis served as references. Among the internationally recognized models for evaluating, the impact of training is the model (Kirkpatrick, DL & Kirkpatrick, J. D, 2009). Also noteworthy are the following: Phillips model (1990), model (Wade, 1999), model (Pineda, 2000), the guide for the evaluation of the impact of the formation of the Inter-American Center for Knowledge Development on Vocational Training of the International Labor Organization (ILO / Cinterfor) (Billorou, Pacheco & Vargas, 2011).
On the other hand, in the Cuban context they highlight: the System of Evaluation and Accreditation of Higher Education (MES, 2018), the instrument for the evaluation of the impact of academic training, proposed by (Ramos et al. 2016), the criteria for the evaluation of the academic impact of master's programs, of (Mestre, 2016), the methodological strategy for the evaluation of the impact of the Master's Degree in Education of the University of Cienfuegos (Lara et al. 2018), the methodology to evaluate the impact in the local development of the Master's Program in Management Accounting at the University of Holguin, Cuba (Sánchez et al. 2018), among others.
As common elements of the aforementioned models, seen as contributions considered in the proposal made, the following stand out:
Among the main limitations of the models studied are:
The study of the theoretical-methodological references on the evaluation of impacts in the formative processes, allowed establishing a set of contributions and limitations that served as a basis for the design of the Impact Assessment System of the Master in Management.
An impact evaluation system was designed for the Postgraduate Academic Program Master in Management, from the University of Pinar del Río, based on theoretical methodological conceptions and made up of nine components, which together will contribute to the continuous improvement of the Program in Quality function
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCES
Añorga Morales, J. (2014). La Educación Avanzada y el Mejoramiento Profesional y Humano. VARONA, Revista Científico-Metodológica, (58), 19-31.
Billorou, N., Pacheco, M., & Vargas, F. (2011). Guía para la evaluación de impacto de la formación. Organización Internacional del Trabajo (OIT/Cinterfor). Recuperado a partir de https://www.oitcinterfor.org/sites/default/files/file_publicacion/guiaevaluacion_imp.pdf
Kirkpatrick, D. L., & Kirkpatrick, J. D. (2009). Evaluating Training Programs. Berrett - Koehler Publishers.
Lara Díaz, L. M., Navales, M. A., & Bravo López, G. (2018). Evaluación del impacto de un programa de maestría para un cambio sostenible. Revista Conrado, 14(63), 101-108.
Mestre Gómez, U. (2016). Criterios para la evaluación del impacto académico de programas de maestría. Didasc@lia: Didáctica y Educación., VII.(5(Monográfico Especial)). Recuperado a partir de https://dialnet.unirioja.es/descarga/articulo/5911162.pdf+&cd=1&hl=es&ct=clnk&gl=cu&client=firefox-b
Ministerio de Educación Superior (MES). (2018). Resolución No.150/18/: Reglamento del Sistema de Evaluación y Acreditación de la Educación Superior. La Habana: autor.
Oficina Nacional de Normalización. (2015). NC-ISO 9000:2015. Sistemas de Gestión de la Calidad Fundamentos y Vocabulario. La Habana: Impresiones ONC. Recuperado a partir de http://www.nc.cubaindustria.cu
Phillips, J. (1990). Return on Investment in Training and Performance Improvement Projects. Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann. 2da. Ed.
Pineda Herrero, P. (2000). Evaluación del impacto de la formación en las organizaciones. Educar, (27), 119-133.
Ramos Azcuy,F. J., Meizoso Valdés, M. del C., & Guerra Bretaña, R. M. (2016). Instrumento para la evaluación del impacto de la formación académica. Universidad y Sociedad,8(2), 114-124.
Rodríguez Gil, A., Mena Lorenzo, J.A., & Lazo Llorente, A. R. (2017). La superación en directivos y reservas de Educación Técnica y Profesional: evaluación de su impacto. Mendive. Revista de Educación, 15(2), 173-183.
Sánchez Arencibia, A., Laguna Cruz, J. A., & Téllez Sánchez, L. (2018). Metodología para evaluar el impacto en el desarrollo local del programa de maestría en contabilidad gerencial de la Universidad de Holguín, Cuba. Avances en supervisión educativa, (29), 1-27. https://doi.org/10.23824/ase.v0i29.620
Wade, P. A. (1999). Measuring the Impact of Training: A Practical Guide to Calculating Measurable Results. Recuperado a partir de https://www.amazon.com/Measuring-Impact-Training-Calculating-Measurable/dp/0787950947+&cd=1&hl=es&ct=clnk&gl=cu&client=firefox-b
![]()
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) Tania Vargas Fernández